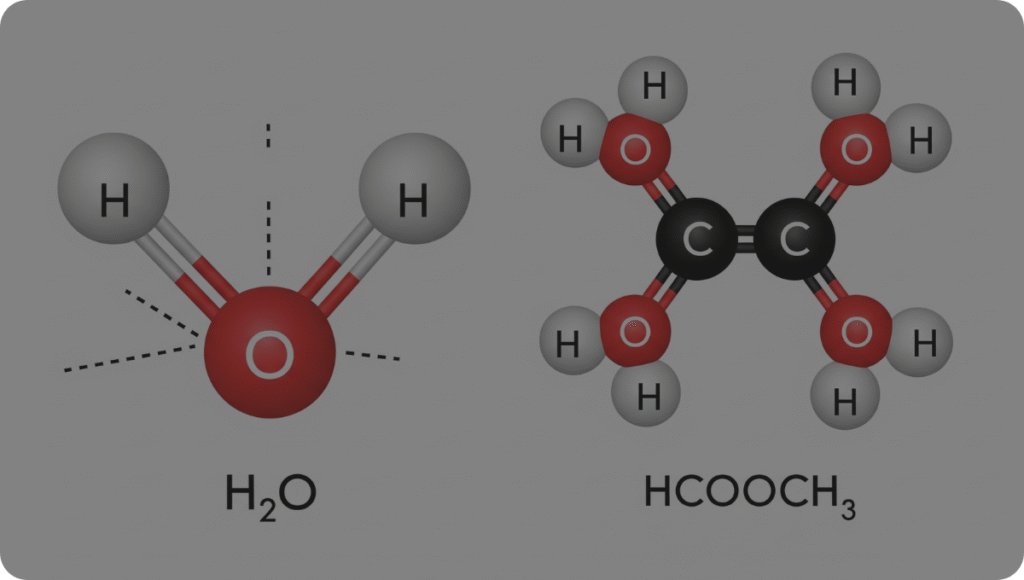
Chemistry can often seem complex, but understanding the structures of molecules like HCOOCH and H2O is fundamental to grasping their properties and roles. In this article, we’ll explore the molecular structures, characteristics, and significance of these compounds in an easy-to-understand way.
What is HCOOCH?
HCOOCH is a simplified notation representing a chemical compound that likely refers to methyl formate (HCOOCH3). Methyl formate is an organic ester created through the reaction between formic acid and methanol. Its structure plays a vital role in organic chemistry, especially in understanding ester functionalities.
Structural Details of Methyl Formate (HCOOCH3)
- Molecular Formula: C2H4O2
- Structural Formula: H–C(=O)–O–CH3
Key features:
- Ester Group: The core part of methyl formate is an ester linkage, characterized by a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to an oxygen atom connected to a methyl group.
- Functional Group: The ester group (–COO–) is responsible for many of its chemical properties, including reactivity and solubility.
What is H2O?
H2O is the chemical formula for water, one of the most abundant and essential molecules on Earth.
Structural Details of Water (H2O)
- Molecular Formula: H2O
- Molecular Structure:
- Water has a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry.
- The oxygen atom serves as the central point, with two hydrogen atoms attached at an approximately 104.5° angle.
Key features:
- Polarity: Water is a highly polar molecule, which explains its solvent properties.
- Hydrogen Bonding: The bent shape allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds, contributing to its high boiling point and surface tension.
Comparing HCOOCH and H2O Structures
| Aspect | HCOOCH (Methyl Formate) | H2O (Water) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Organic ester | Inorganic molecule |
| Shape | Trigonal planar around the carbonyl carbon | Bent (~104.5°) |
| Polarity | Polar due to ester group | Highly polar |
| Bonding | Covalent bonds, ester linkage | Covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds |
| Functionality | Used in organic synthesis, solvents | Essential for life, solvent |
Significance of These Molecules
- Methyl Formate (HCOOCH):
- Used as a solvent in chemical reactions.
- Serves as a starting material in organic synthesis.
- Found naturally in some biological processes.
- Water (H2O):
- Vital for all known forms of life.
- Acts as a universal solvent.
- Involved in countless chemical reactions.
Conclusion
Understanding the structures of HCOOCH (methyl formate) and H2O (water) provides insight into their chemical behavior and roles. While methyl formate is an organic ester with a planar structure and ester functionalities, water is a simple bent molecule characterized by hydrogen bonding and polarity. Recognizing these structural differences helps in appreciating their unique properties in chemistry and everyday life.
If you want to explore more about molecules and their structures, stay curious and keep learning!